Your body is constantly exposed to bacteria, viruses, and other harmful invaders. Yet most of the time, you stay healthy — thanks to the powerful protection of your immune system. The immune system is a complex network of cells, organs, and proteins that defend the body against infections and keep you safe from diseases. Without it, your body would not be able to survive the countless threats you encounter every day.
In this blog, you will learn what the immune system is, how it works, its key parts, and how you can strengthen your immunity naturally. This guide is simple, accurate, and perfect for anyone who wants to understand their health better.
What Is the Immune System?
The immune system is the body’s natural defense system. Its main job is to identify harmful germs, attack them, and remove them before they cause illness. These germs can include:
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Fungi
- Parasites
- Toxins (harmful chemicals)
The immune system works 24/7, scanning your body for anything that does not belong — like a highly trained security force.
How the Immune System Works
The immune system works in a step-by-step process:
1. Recognition
When a germ enters your body, your immune system first identifies it as harmful.
2. Response
White blood cells immediately move toward the invader to destroy it.
3. Defense
Special proteins called antibodies lock onto the germ and help remove it.
4. Memory
After fighting an infection, your immune system remembers the germ.
If the same germ enters again, your body responds much faster.
This is the reason vaccines work — they train your immune system without making you sick.
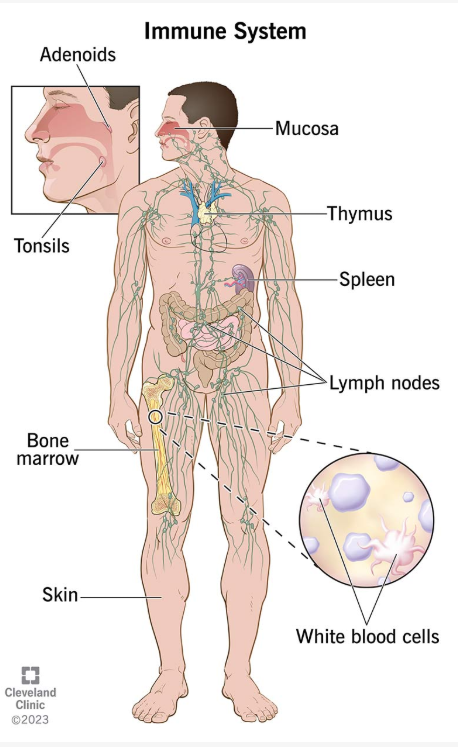
Main Parts of the Immune System
The immune system has many parts, each with a unique role. Together, they keep your body protected.
1. White Blood Cells
These are the main fighters of the immune system.
They detect, attack, and destroy germs.
There are different types of white blood cells, such as:
- Neutrophils
- Lymphocytes
- Macrophages
2. Lymphatic System
This is a network of tissues and organs that carries immune cells throughout the body. It includes:
- Lymph nodes
- Lymph vessels
- Tonsils
- Thymus
- Spleen
The lymphatic system filters harmful substances and produces important immune cells.
3. Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is the soft tissue inside bones that produces:
- White blood cells
- Red blood cells
- Platelets
All immune cells begin their life in the bone marrow.
4. Skin and Mucous Membranes
Your skin is the body’s first line of defense.
It blocks germs from entering.
Mucous membranes in your nose, throat, and lungs trap germs before they can spread.
5. Antibodies
Antibodies are proteins made by the immune system.
They recognize germs and help destroy them.
Each antibody is designed to fight a specific germ.
What parts of your body make up the immune system?
Many parts of your body, including immune system organs and cells, work together to keep you healthy. The main components of your immune system are:
- White blood cells. These immune system cells attack and eliminate harmful germs to keep you healthy. There are many types of white blood cells, and each type has a specific mission in your body’s defense system. Each type also has a different way of recognizing a problem, communicating with other cells and getting their job done.
- Antibodies. These proteins protect you from invaders by binding to them and initiating their destruction.
- Cytokines. These proteins serve as chemical messengers that tell your immune cells where to go and what to do. Different types of cytokines do different specific tasks, like regulating inflammation. Inflammation happens when your immune cells are warding off invaders or healing damage to your tissues.
- Complement system. This is a group of proteins that teams up with other cells in your body to defend against invaders and promote healing from an injury or infection.
- Lymph nodes. These small, bean-shaped organs are like colanders you use to drain pasta. They filter waste products from the fluid that drains from your tissues and cells (lymph) while keeping the good components, like nutrients. You have hundreds of lymph nodes throughout your body, and they’re a vital part of your lymphatic system.
- Spleen. This organ stores white blood cells that defend your body from invaders. It also filters your blood, recycling old and damaged cells to make new ones.
- Tonsils and adenoids. Located in your throat and nasal passage, tonsils and adenoids can trap invaders (like bacteria or viruses) as soon as they enter your body.
- Thymus. This small organ helps T-cells (a specific type of white blood cell) mature before they travel elsewhere in your body to protect you.
- Bone marrow. This soft, fatty tissue inside your bones is like a factory for your blood cells. It makes the blood cells your body needs to survive, including white blood cells that support your immune system.
- Skin. Your skin is a protective barrier that helps stop germs from entering your body. It produces oils and releases other protective immune system cells.
- Mucosa. This three-layered membrane lines cavities and organs throughout your body. It secretes mucus that captures germs.
Types of Immunity
There are two main types of immunity:
1. Innate Immunity (Born With It)
This is the body’s natural defense system you are born with.
It reacts quickly but is not specific to any particular germ.
2. Adaptive Immunity (Developed Over Time)
This develops as you grow.
Your immune system learns to fight specific germs and remembers them.
Vaccines help build adaptive immunity safely.
Why the Immune System Is Important
A strong immune system:
- Prevents infections
- Fights diseases
- Helps wounds heal
- Removes dead or damaged cells
- Protects your body from harmful substances
When the immune system is weak, infections become more frequent and harder to control.
Signs of a Weak Immune System
You may have a weakened immune system if you frequently experience:
- Constant colds or infections
- Slow wound healing
- Fatigue
- Digestive issues
- Allergies
- Frequent fever
If these symptoms persist, it is important to consult a healthcare professional.
How to Keep Your Immune System Healthy
A strong immune system depends on your daily habits.
Here are proven ways to boost immunity:
1. Eat a Balanced Diet
Include foods rich in vitamins and minerals such as:
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Nuts and seeds
- Whole grains
- Lean proteins
2. Sleep Well
Aim for 7–9 hours of sleep.
Poor sleep reduces your body’s ability to fight infections.
3. Exercise Regularly
Physical activity improves circulation and strengthens immune response.
4. Manage Stress
Chronic stress weakens immunity.
Practice deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
5. Stay Hydrated
Water helps remove toxins and supports overall immune function.
6. Avoid Smoking and Excess Alcohol
These weaken the body’s defenses and make infections more likely.
7. Practice Good Hygiene
Wash your hands regularly and keep your environment clean.
Common tests that check the health of your immune system
Healthcare providers often use blood tests to check how well your immune system is working. Specific blood tests your provider may order include:
- Antibody test.
- Complete blood count.
- Complement blood test to check levels of specific types of protein in your blood, such as C3 proteins.
The immune system is one of the most important systems in the human body. It protects you from harmful invaders, helps you recover from illness, and keeps you healthy every day. Understanding how it works allows you to take better care of yourself.
By eating well, sleeping enough, managing stress, and staying active, you can naturally strengthen your immunity and improve your overall health.